

They are therefore called domain-specific.Īn example of a general-purpose language is C++. Other languages are tailored to some specific application domain. This is why they are called general-purpose. Some programming languages are designed to build software that can solve any problem and perform any task. This distinction is quite easy to understand. General-purpose vs Domain-Specific Languages Automatic Memory management vs Manual management.Procedural vs Functional vs Object-Oriented.Here’s the list of the concepts we will master: What does it mean that Java is object-oriented? What about the fact that is general-purpose? To understand the whole picture means to understand what are the main features of a language. Then, every language is basically a different implementation of several among these concepts, to provide an original result. These are theoretical concepts, well defined in books about languages theory. For example, Java is a general-purpose, high-level, statically typed, object-oriented, compiled to bytecode, programming language.Įach of those definitions specify a particular feature of Java’s. This why we use many words to describe a single language. Programming Languages are very complex systems, where many features interact and provide a (hopefully) consistent result.
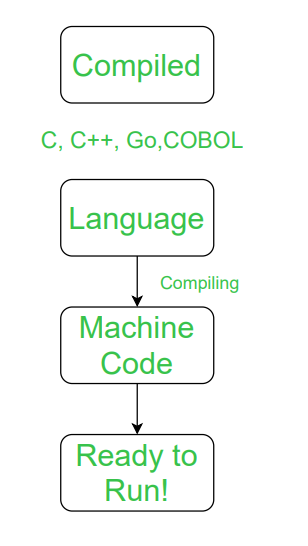
Whether you want to design a new programming language, or you want to study Compilers theory, or you just want to learn a new language, the first and perhaps most important thing to do is to understand the whole picture.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
